
The burning away of this layer may cause compartment syndrome, resulting in further nerve and muscle damage.
4th degree burn treatments skin#
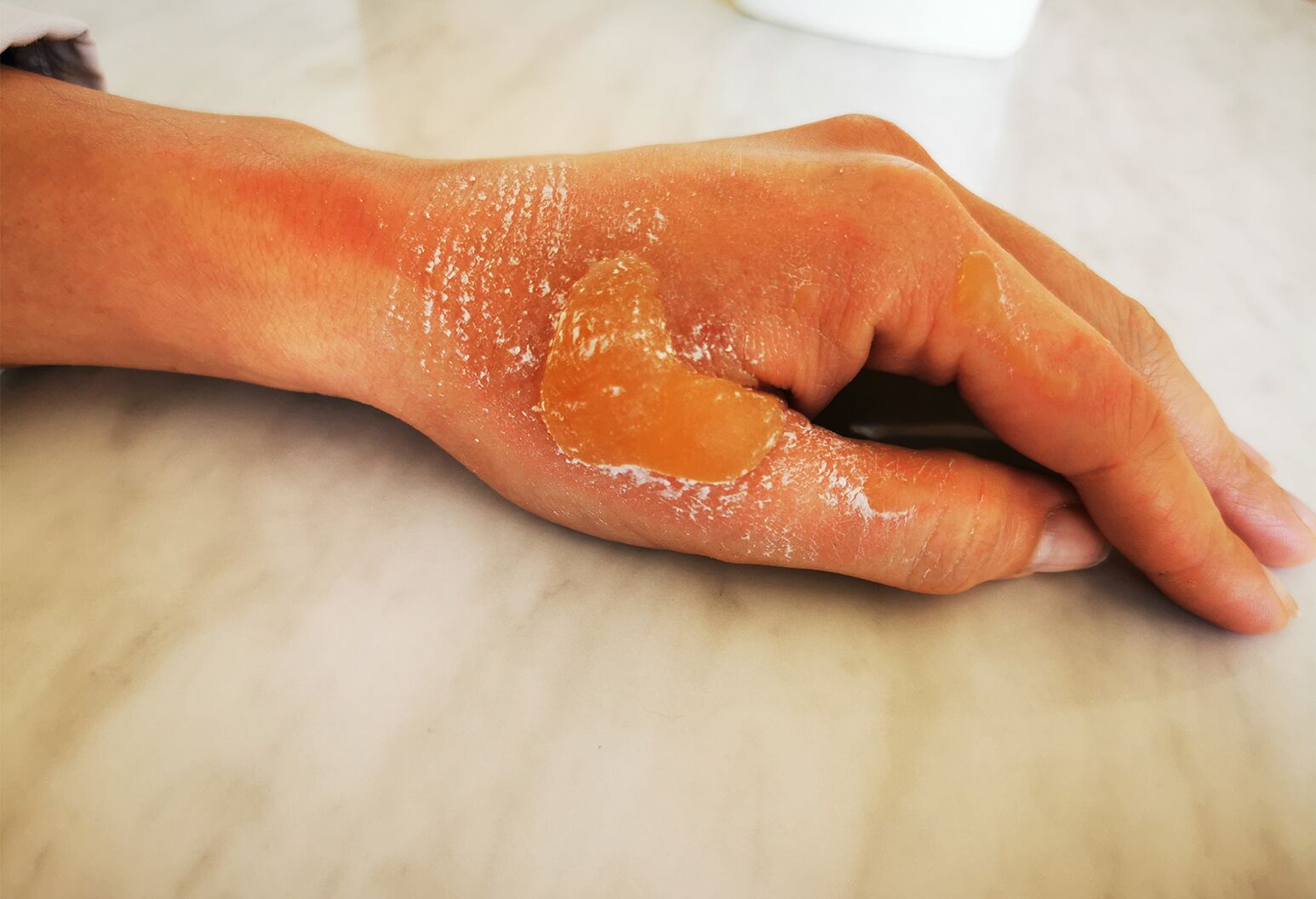
The hypodermis is the deepest layer of skin that is closest to the muscles. In the case of fourth degree burns, the hypodermis may be burned away. In some cases, infection may enter the blood stream and cause sepsis, which can be life threatening. This can cause dehydration and lack of oxygen, or complications from low blood volume.ĭamage to tissue, blood vessels, and bones can result in permanent damage to limbs.

If major blood vessels are destroyed by burns, lack of blood circulation may result. Third and fourth degree burns have a high risk of infection and may cause the patient to go into shock. Both types of burns will result in partial or total burning away of the skin in the area, and the surrounding skin will often appear blackened and charred. Fourth degree burns may expose muscle tissue or even bone. Third degree burns will expose the adipose, or fat, tissue beneath the dermis layer of skin. Third and fourth degree burns are identifiable by the deterioration of skin and exposure of underlying tissues. Failure to treat burns quickly can also allow some burns of lesser severity to worsen. In some cases, exposure to an intense burst of electricity or ultraviolet rays will cause third or fourth degree burns. Third and fourth degree burns are typically caused by prolonged exposure to the source of the burn, such as fire, chemicals, or hot liquid. Due to nerve damage, patients may not feel any pain when suffering from third or fourth degree burns. Third degree burns affect tissues and nerves, and fourth degree burns may even extend into bone. Third and fourth degree burns are extremely severe burns that should be treated as soon as possible by medical professionals.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
